Alphabet Inc. has embarked on the biggest bond issue in its corporate history of $20 billion to accelerate innovation in artificial intelligence (AI) technologies that is re-evaluating the technology industry.
The seven-cycle offering, maturing between 2029 to 2066, will indicate a change of approach by leading technology companies, who will shift their reliance on high cash piles to the utilization of debt financing in reaction to increment of expenses linked to AI infrastructure.
Said Lale Akoner, global market analyst at eToro.
Century bonds are usually the preserve of governments or regulated utilities with very predictable cash flows, so this deal shows that, at least for now, investors are willing to take on very long-dated risk tied to AI investment
Corporate Borrowing Development in the Technological Bow
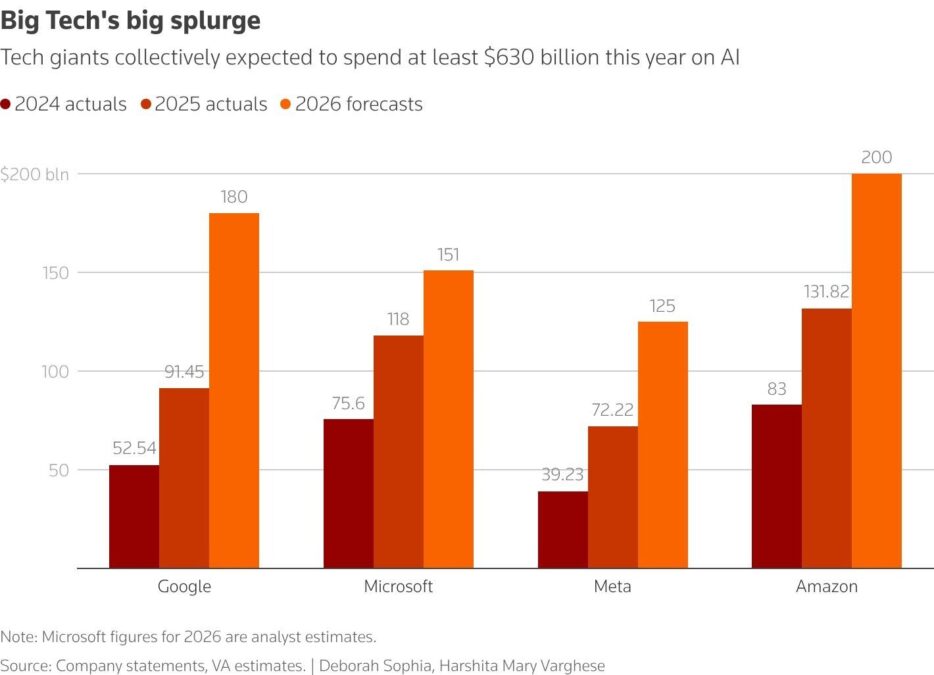
In the past, successful companies like Alphabet, Microsoft, Amazon and Meta have funded their innovation budgets by strong cash flows. Over the last few years, these companies have embraced the use of bond markets as one of its major sources of funds.
The firms will spend no less than $630 billion in capital expenditure in the current fiscal year, which is largely on data centers and AI processors, with high power consumption.
The announcement by Alphabet also reinforces the statement by Oracle last 2 February of issuing $25 billion notes and is supported by the agreement in the issuance of AI hyper capital corporates of $121 billion of corporate bonds in the prior year as reported by BofA Securities.
Alphabet declared it would increase capital-expenditure target to $175-$185 billion by 2026, which is more than the sum of the three years before it.
The Reception of Investors and the Dynamics of Yield
The bond offering had a huge demand that hit highest orders of over $100billion. However, there is still anxiety about the relationship between AI-related spending and the returns to be expected to those spending since no significant productivity gains have been realized so far.
The recent issue is an indication that investors are ready to take on long-term maturities of AI projects. Another major issuance of a technology firm that Alphabet is considering is the historic issuance of a 100-year bond, the first of its kind issued by a technology company since the dot-com age.
Strategic Risk and Reward Implications
The intensive debt activity portrays the criticality of the technology sector adoption of AI. They predict that by 2028, AI infrastructure investment in the top-end of investment banking may reach $3 trillion, according to forecasts of large investment banks like Morgan Stanley.
The success of the Alphabet debt strategy will hinge on the ability to leverage on the growing cloud and AI needs, which is currently being experienced in the rising revenues of Alphabet. With the potential gains in productivity, bond yields will pay off very well; on the other hand, there will be a major credit risk in the borrowing of funds thus putting strain on balancing sheets.
By the end of February, 2026, the debt strategy at Alphabet will be backed by investors but the final test would be whether the company will be able to meet the AI-driven transformational goals.




